
Onychomycosis is a widespread fungal nail disease (up to 18% of the population). It affects people of all ages, and an increase in the number of adolescents and children has also been noted over the past decade. Due to the high contact and frequent relapses, the treatment of nail fungus on the hands and feet is a complex and time-consuming process.
When does the infection occur?
- In families with a general use of shoes, household items (rugs in the bathroom) and body care products (wipes, manicure sets);
- When visiting swimming pools, showers in gyms and companies, saunas and baths.
Causative agents of the disease
Effective treatment of nail fungus is possible only with the correct laboratory diagnosis of the pathogen. In almost 90% of cases, nail fungus is caused by various types of dermatophytes. A specific species affects the corresponding body parts that are characteristic of it:
- toenails and fingernails, as well as any part of the skin;
- nail plates on the feet and skin of the III-IV interdigital spaces, the arch of the foot, the upper third of the sole, the lateral surfaces of the toes.
In more rare cases, the disease is caused by other types of fungi - trichophytos, epidermophytos, much less often - similar to yeast. Very rarely, onychomycosis can be caused by mold affecting the nails in the area of the first fingers, mainly in people over the age of 50.
Contributing factors
Favorable conditions for the introduction and development of infection:
- Damage to the nail plate and surrounding skin. This often happens due to the use of tight shoes, cosmetic procedures.
- Fractures of the fingers and bones of the foot or hand.
- Swelling of the legs with heart disease, obliterating atherosclerosis of the lower limbs, varicose veins, Raynaud's disease (spasms of the arteries of the upper limbs).
- Endocrine diseases (especially diabetes mellitus).
- Pregnancy (due to hormonal changes and decreased immunity).
- Decreased general immunity.
- Congenital anomalies in the formation of the stratum corneum of the skin.
- Serious and long-term chronic diseases that reduce the body's defenses.
- Long-term treatment with corticosteroid drugs and antibiotics, systemic diseases and other immune diseases.
The possibility of transmission of the infection in the body itself by blood and lymph has already been proven.
Onychomycosis diagnostics
Diagnosis of a fungal infection is based on local and general clinical manifestations and laboratory research.
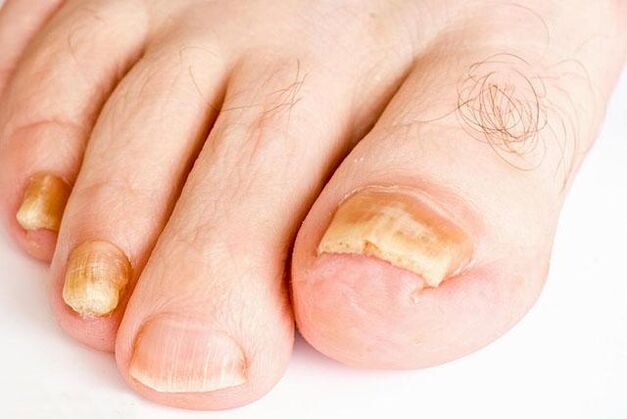
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms are very different and depend on the type and type of pathogen. Separately, toenails (80%) and fingernails can be affected; less common is the simultaneous defeat of the nails of the lower and upper extremities.
Depending on the nature of the change in the nail plate, 4 forms of damage are distinguished:
- Normotrophic- characterized by a yellowish discoloration of the terminal edge of the nail plate. It becomes dull and thickened due to the epidermal stratum corneum (subungual hyperkeratosis). The shape of the affected nails does not change for a long time.
- Hypertrophic, in which the nail becomes yellowish and thickens, the edges become loose. The transverse streak gradually appears. The nail plate becomes dull gray and dull. In some cases, (usually on the first toes) it thickens, becomes long and curved like a bird's claw or beak (onychogryphosis).
- Atrophic- the nails are dull, greyish or yellow. They change shape, collapse at the end, partially exposing the bed. The latter is covered with loose layers of the stratum corneum.
- Onycholysis- detachment of the nail plate from the bed. With this form of fungal infection, normal color remains only in the root area. The rest of the nail thins, peels off the bed, loses luster and becomes yellowish or grayish-dirty.
Combined forms are often observed. The clinical manifestations listed are not specific to specific types of fungal lesions. They can also be in diseases not associated with fungi.
Some common manifestations are also possible: an allergic rash on the body, increased fatigue and decreased appetite. They are explained by the ability of some types of dermatophytes to cause allergic restructuring of the body and mold of fungi - to release toxins, leading to chronic intoxication of the whole body.
Laboratory diagnostics
It consists in the collection of material (particles of layers of the epidermis, pieces of nails). The taken material is poured with a caustic alkaline solution, left for 24 hours at a temperature of about 20 degrees, after which it is examined under a microscope. This technique allows the differential diagnosis between fungal and non-fungal lesions. In the presence of a fungus, filaments of various thicknesses and shapes, groups of spores are visible under the microscope.
After that, the material is sown on a special nutrient medium for the growth of the pathogen, followed by the identification of its type and the determination of sensitivity to antifungal drugs.
Characteristics of the treatment
The choice of therapy methods takes into account the form, type and extent of the lesion, the growth rate of the nail, the general condition of the body and the side effects of the drugs used, especially in the presence of concomitant diseases. Based on these principles, the treatment of toenail fungus, as well as of the hands, consists of a local or complex effect.
Local impact principles
It is possible if:
- the infection did not affect all the nails;
- the defeat of each of the infected nails is less than half of its area;
- the process is found only on the terminal and lateral sections of the plate without involving the root;
- there are contraindications to the use of systemic drugs.
Local drug treatment
It consists of using a cream, solution or nail polish containing substances that soften the nail plate. They also include drugs for the treatment of toenail (hand) fungus, which suppress the growth and development of the infection:
You can pre-apply any preparations to soften the plate and remove it layer by layer, as in the first case, then 2 times a day apply broad-spectrum antifungal drugs in the form of creams or solutions. At the same time, it is necessary to rub them into the surrounding skin.
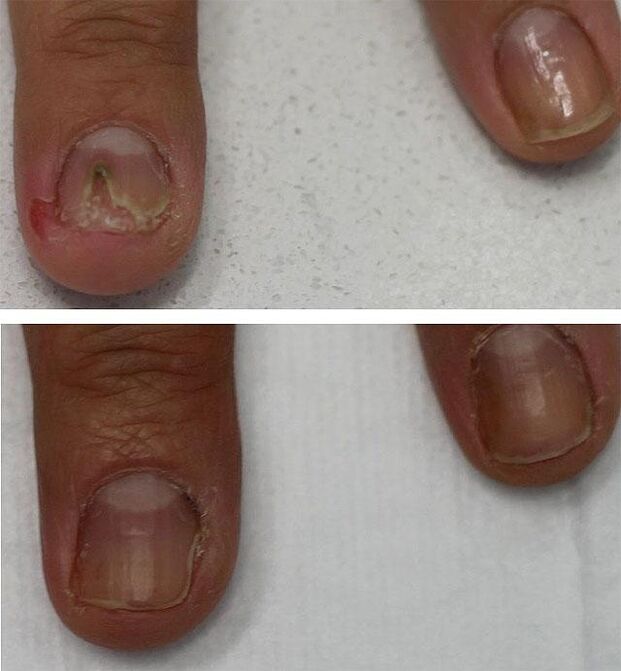
Medical hardware pedicure
As an additional procedure (but not as a treatment! ) A medical pedicure is used which reduces the treatment time. Its essence is to use a router with an attachment in the form of a metal or diamond cutter. This device greatly facilitates the painless removal of a previously softened nail from its bed. The use of the hardware method is advisable when more than 60% of the area of the nail plate is damaged, but it does not replace further drug treatment with antifungal agents.
Surgery
In case of severe forms of onychomycosis with severe deformation of the nail, it is sometimes surgically removed under general anesthesia or conduction anesthesia with further use of antifungal drugs. The main disadvantage of the method is damage to the nail bed, as a result of which the newly grown plate lags behind and has an irregular shape.
Laser treatment
This method consists in heating the nail with laser radiation in a range of short pulses up to a temperature of 45-47 degrees, at which dermatophytes die. The procedure is most effective in the initial stages of nail damage without deformation. Depending on the severity, 1 to 8 sessions should be performed with an interval of 7 to 60 days. In case of severe injuries, local and systemic treatment must be carried out.
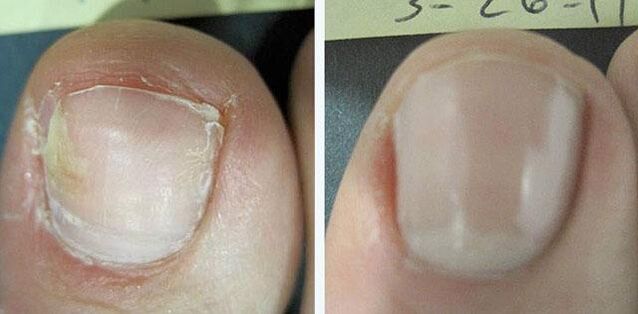
Systemic drug therapy
It is indicated for multiple nail lesions, root involvement in the process and in the absence of the effect of local exposure.
The most effective drugs for the treatment of nail fungus are tablets. containing substances such as terbinafine, fluconazole and others. They are prescribed in courses for 3-4 months and remain in the body after the end of treatment up to 9 months. The last two drugs, due to the toxic effect on the liver, are used much less frequently.
Systemic treatment is contraindicated in kidney and liver diseases. During pregnancy and lactation, only local treatment of 1-2 nails is possible, but it is better to refrain from this.

























